2852 Alton Pkwy, Irvine, CA 92606
2852 Alton Pkwy, Irvine, CA 92606
INTRODUCTION

Immunoblotting (alternatively, Western blot, line-ELISA, dot-blot or cold-blot) is an analytical technique used to detect specific proteins in a patients’ sample. The proteins to be analyzed are dispensed onto a membrane (typically nitrocellulose, nylon or PVDF), where they are probed by the antibodies of the patient. A simple secondary antibody conjugated to a reporter dye forms the basis of the color reaction which can be read by eye (qualitative) or instrument (qualitative and quantitative).
In the field of diagnostics their use is widespread as a screening tool where a patient can be profiled against multiple markers simultaneously. Common Immunoblot screening applications include:
- Allergies
- Cancer Biomarkers
- Autoimmune diseases
- Food intolerance
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)
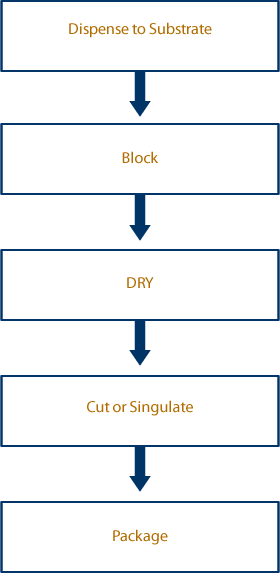
BioDot are at the forefront of the production of Immunoblot diagnostic tests. From a small batch R&D platforms up to large multi-dispenser (32 channels) batch platforms or Reel to Reel systems for full scale production. Typically proteins (and sometimes DNA) are deposited by a contact or non-contact BioJet Plus dispenser. Once dispensed the ‘blots’ are blocked then dried. The product is then cut into small strips for their assembly into cassettes.
- FrontLine or BioJet technology for dispensing the lines
- AirJet equipped dispensing platforms for blocking
- Forced air ovens (with IR sensors) for drying
- Guillotine, rotary cutters and sheet slitters for singulation of tests.
Applications Flow Diagram