INTRODUCTION
The development of manufactured protein arrays is currently getting a lot of visibility due to the existence of an immense field of applications, including biosensors, diagnostics applications such as serum-based diagnostics, and pharmaceutical target design. The latter typically involves the study of protein targets through protein-protein interactions, enzyme-substrate reactions, receptor-ligand interactions, and drug-target binding. Protein microarrays can also be used to miniaturize and multiplex immunoassays and have performed better than enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays in both sensitivity and quantitative range for use in immunoassays.
A common operation in multiplexing is gridding proteins onto a substrate in an ordered array. Once arrayed, the substrate is probed with a fluorescent probe of interest, and is then analyzed to detect the locations where the probe bound to the substrate. An alternative to pin gridding, the most common means of achieving high-density arrays, is to use either BioJet Plus or Scienion for a non-contact dispense. Patented BioJet Plus technology involves the coupling of a microsolenoid valve to a high resolution syringe. The system is then synchronized with the XYZ motion allowing for very fast dispense with high accuracy and precision. Scienion dispensing is based on piezo technology that is also very fast. The Scienion technology dispenses from the picoliter range to the low nanoliter range, while as the BioJet Plus technology dispenses from the low nanoliter range to the low microliter.
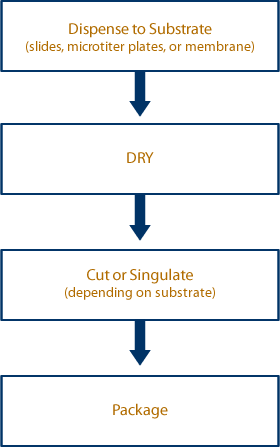
Applications Flow Diagram
 2852 Alton Pkwy, Irvine, CA 92606
2852 Alton Pkwy, Irvine, CA 92606
 2852 Alton Pkwy, Irvine, CA 92606
2852 Alton Pkwy, Irvine, CA 92606

